Broadband SoHo FTTx
Tutorial
FTTH / FTTP
(Fiber to the Home / Fiber to the Premise) is a fiber-optic
broadband triple play service (Voice/Data/Video) currently
in deployment throughout the U.S. by various RBOC's such as
Verizon, AT&T, and individual city municipalities. The
architecture of this deployment is called a PON (Passive
Optical Network), this is a completely passive (the signal
is transported by laser with no electronics) network
consisting of fiber optic cabling, passive splitters,
attenuators, and couplers. These listed components are
also referred as the ODN (Optical Distribution Network)
elements that distribute an optical signal through a
branched topology to an ONT (Optical Network Terminal). This
architecture is a point-to-multipoint system that allows a
maximum of 32 ONT's to be serviced, with a OSP topology of
1x32 Home Run Split, 1x4 to 1x8 Distributed Split, or 1x8
to 1x4 Distributed Splitter configuration.


**This entire FTTx
section was updated 10/1/08
Note:
This tutorial was created to give a basic overview to
a new field technician or client of this technology, and
describe various deployment components that form this
next-generation network. Please be aware that we are only
describing some key points that customers have commonly
questioned that pertain to the recent RBOC's deployment. Please refer to some of the links below for a
complete PON overview.
To all that have viewed, and promoted this tutorial ...
Thank You !
Various FTTx PON Deployments
(Tellabs) Architecture Example -
Click Here
FTTx ~ Fiber to the x ,
is the deployment of fiber (optical) cable to a specific
location (proximity) in regards to the customer premise. The
“X” is used to describe the specific application of the
service. As you will read in magazines and various articles
you will see these following terms below and used loosely,
as some relate to each other, or just acronyms.
FTTc ~ Fiber to the Curb , is the deployment of fiber close
to the customer but not fully to the customers residence. In
this deployment the existing copper plant is still used to
deliver service to the actual customer. FTTN (Fiber to
the Neighborhood) & FTTC (Fiber to the Cabinet)
generally fall under the FTTC category. Both services are in
deployment and in use, a perfect example is a DLC/NGDLC
(Digital Loop Carrier) which some of us get our phone
service from. A direct fiber from the CO (Central Office) is
terminated at the DLC/NGDLC and then service is delivered to
the customers residence via the copper plant.
FTTn ~ Fiber to
the Node (AT&T U-verse)
U-verse (ATT) is an example
of a widely deployed FTTn system. This architecture was
chosen by them to extend the fiber link as close to the
neighborhood existing SAI terminal (distributes
individual cable pairs to each customers residence) for
triple-play service. The fiber link is extended with the
help of the
Alcatel 7330 ISAM
(Intelligent Services Access Manager) which resides in an
outdoor cabinet commonly called a VRAD, the ISAM converts
the service to
VDSL-2, which is then
cross-connected to the customers existing copper POTS line.
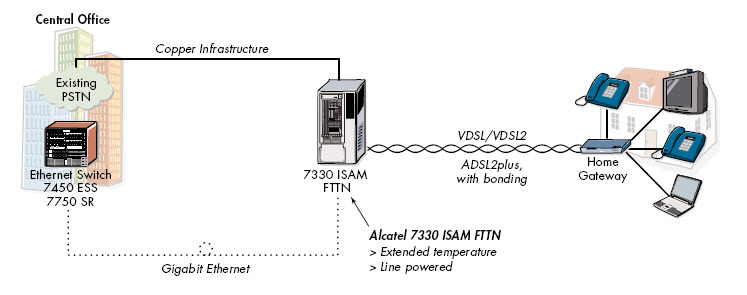
(Alcatel Lucent) - FTTN
Architecture
The Economics of FTTN vs. FTTP
- (ADC) White Paper
FTTb ~ Fiber to the Building
, is the deployment of fiber (optical) cable to a specific
location within a building, then connected to the buildings
existing copper, cable facilities. This deployment is also
referred to as FTTB (Fiber to the Basement) & FTTB (Fiber to
the Business). This deployment will be the typical for MDU’s
& MTU’s also known as **
FTT mdu ~ Fiber to the MDU **
FTTh ~ Fiber to the Home
, is the complete deployment of fiber to the customers home, with replacement of there existing NID (Network Interface
Device). This replacement device is called an ONT (Optical
Network Terminator).
FTTp ~ Fiber to the Premise
, is a loosely used term. It can
be the definition of FTTB or FTTH, it depends on how the
context is used and specific location of where the fiber
terminates. In general it falls under the FTTB definition.
Passive Optical Network Components
Below are the primary
components that create a passive-optical network. As they
are explained please read the following associated documents
so you can see the physical component and achieve a better
understanding of its role in the network. We recommend that
you view the
Verizon FTTP Tutorial to
see their chosen network component brands. As you will
notice you may come across various FTTx vendor equipment as
a field technician, but they are generally the same, and
perform the same function.
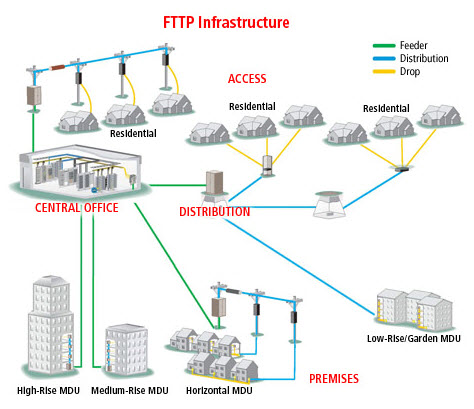
(ADC)
- FTTP Infrastructure
OLT
~ Optical Line Terminal , is the networks control
processor. This unit resides in the local CO (Central Office)
cross connected to the video and data networks that will be
delivered to your home, it consists of a special DFB
(Distributed Feedback) calibrated laser that is always on.
The OLT control card acts as a traffic signal to the remote ONT's for complete data / video throughput upstream and
downstream. (Tellabs) OLT -
Click Here
(Tellabs) OLT OSP Cabinet -
Click Here
ODN
~ Optical Distribution Network , is part of the OSP
architecture components. The actual fiber-optic cabling,
passive splitters, FDH, attenuators and couplers.
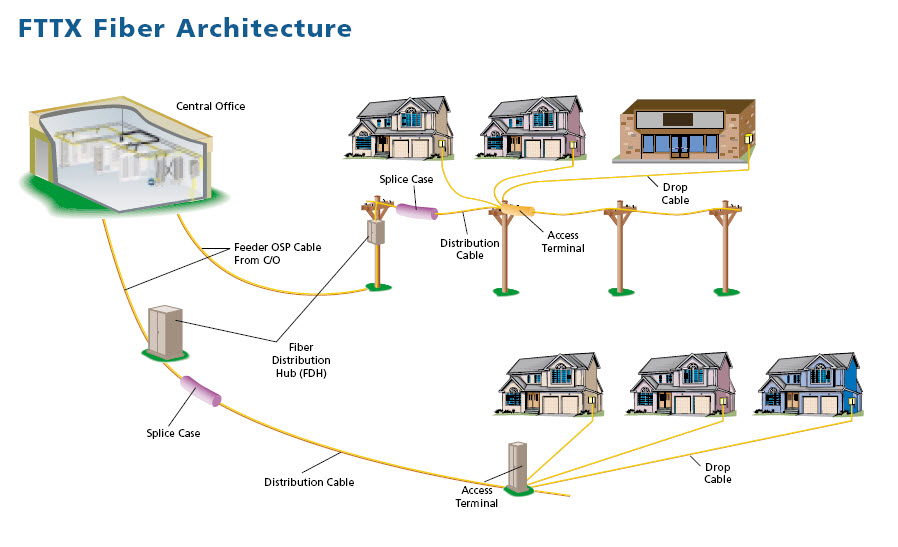
(ADC)
- FTTx
Architecture
FDH
~ Fiber Distribution Hub , is the cross
connection splice-point for
the Central Office Fiber and Distribution Fiber to the
FDT's servicing the customers community. This hub can come in various configurations
(Aerial Pole mount / Ground Pedestal), the providers configuration will
typically be the 144 / 216 user
count, designed to be a plug and play system for the FDT
/ Drop Cable connections.
(ADC) FDH Picture -
Click Here
(ADC) FDH Open -
Click Here
(ADC) FDH Rear Panel -
Click Here
FDT
~ Fiber Distribution Terminal , is the cross
connection splice-point between the community serving FDH
Distributing Cable, and the Drop Cable to the
customers ONT. Tech Note - The FDT is aka
"Access Terminal", this term is used loosely.
DROP CABLE ~
This cable is the final connection to the customers ONT.
This cable can be spliced from an aerial / underground FDT.
Most providers have moved to a
pre-terminated drop cable system,
this saves cost and installation time.
ADC - MST System
ONT
~ Optical Network Terminal , this is the CPE
(Customer Premise Equipment) endpoint of the ODN. The ONT
is an Optical to Electrical to Optical device, that
delivers your triple play services. It will replace your
existing copper NID (Network Interface Device) , and coax
connections. The existing POTS / Coax inside wiring will be cross connected to
the SFU (Single-Family Unit) ONT.
Since we understand that a PON is completely passive the
endpoint must contain an AC voltage connection to perform
the Optical to Electrical conversions for your services. Ex.1
(Siemens) ONT Picture -
Click
Here
Ex.2
ONT Picture -
Click
Here
MDU - Passive Optical Network
Components
Above we listed the
primary components that create a passive-optical network,
and they are the same for an MDU deployment. Within the last
year the FTTx MDU market has produced a vast amount of
products. The only differences in the MDU deployment are the
FDT's, Drop Cables, and ONT's.
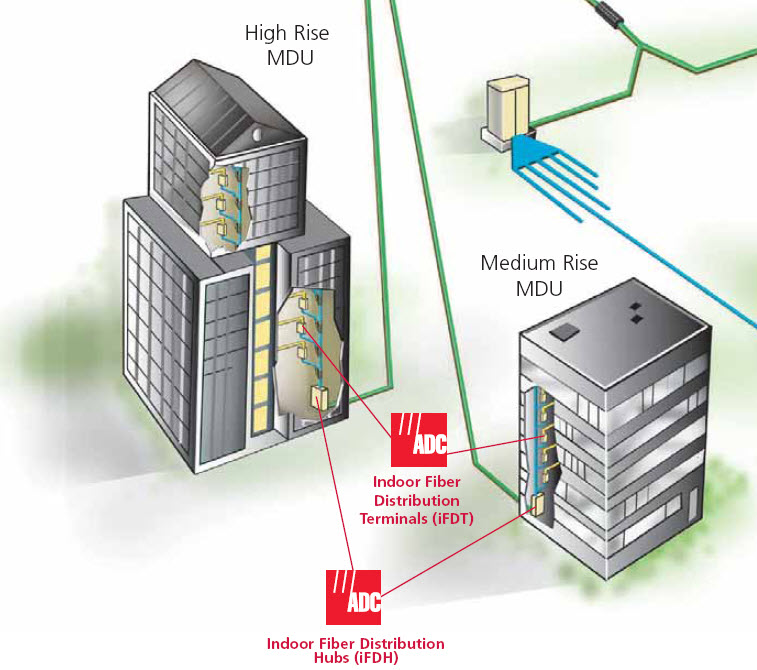
(ADC)
- FTTx MDU
Architecture
iFDH
~ Indoor Fiber Distribution Hub , same as FDH,
just an indoor unit.
iFDT
~ Indoor Fiber Distribution Terminal , same as
FDT, just an indoor unit.
Drop Cable ~
This cable will enter the customers apartment from the
FDT that's usually located in a closet, or stairwell in a
high-rise building. In a small garden-style MDU deployment
your drop cable may come from an
FDT located on the outside of your building, and routed through the roof breezeway into
your apartments designated closet.
ONU
~ Optical Network Unit , this is similar to
the SFU-ONT but for a MDU / MTU, or small business. It
contains 12 - 24 POTS Lines, multiple "Ethernet" or "VDSL" connections, and one / two high-powered RG video
outputs.
These ONT's come in two forms, a wall mountable or
rack-mountable unit, they are typically installed in a
stairwell area, or basement next to the existing SAI for
that floor.
Ex.1
(Siemens) ONU Picture -
Click
Here
ADC - RealFlex Drop Cable System
* The video below is from
ADC, and contains
a very detailed description of how important the Drop
Cable is in the MDU network.
PON Transport Operation
FTTx is not
a new technology, it has been around for sometime within
the RBOC's (Bell South was one of the first to experiment
with FITL and implement this service back in the late 80's)
but as years have passed the technology has advanced along
with the reduction cost of fiber, creating what is the
broadband craze of today. With this sudden craze and endless
possibility of bandwidth , you should keep in mind a few
several things. Fiber has the ability of offering a huge
bandwidth , but within a PON there are several formats with
limitations. These formats are APON (ATM-PON) , EPON
(Ethernet-PON), and GPON (Gigabit-PON) each has a unique
set of features and transport process. At this time there
is still a huge debate as to which format is the best and
what should be the standard, but at this time most
deployments are currently BPON, future deployments by the
first of next year will generally be GPON if within the
providers budget.
BPON
- PON FSAN / ITU-T G.983
-
Fiber
Cable Span no more than 20Km (12Miles) of Single-mode
fiber
-
Asymmetrical 622 (OC-12) / 155 (OC-3) Mbs bandwidth per
OLT path of 32 ONT's
-
OLT -
WDM (Wave Division Multiplexing)
-
1550nm
(1480-1580) for downstream
-
1310nm
(1260-1360) for upstream
-
TDM
(Time Division Multiplexing) of ATM packets
-
1:32
Passive Splitter OSP Topology
GPON
- PON FSAN / ITU-T G.984
** Note:
These services can also be configured symmetrical also but
the most common deployments will be asymmetrical.
Listed
below are some recommended industry links to help in your
further knowledge of this growing technology. As time
permits I will update these links, for more examples of the
passive optical network components please visit the
Verizon tutorial.
Legal
Note:
Below are registered trademark
logos for the following companies. This tutorial was created
with the use of their unique company logos,
and documents that
discuss products, such as data sheets, white papers and spec
sheets, and on product advertisements. With respect to this
and the tutorial created, do not republish or use any part
of this out of its context. To obtain further information on
the products discussed in this tutorial, please click on the
companies logo for that desired product.




